Experiencing high CPU usage from the Antimalware Service Executable High CPU can be a significant concern for Windows users. Known as MsMpEng, this crucial background process is an integral part of Windows Defender, working tirelessly to scan and protect your system from malware threats. While its protective measures are essential for your device’s security, they can sometimes lead to frustratingly high CPU usage, impacting the overall performance and responsiveness of your computer. This article delves into common Windows security performance issues, particularly those arising from excessive Antimalware Service CPU usage, and offers effective solutions to tackle these challenges. If you’re seeking to reduce CPU usage in Windows 10, you’ve come to the right place for practical tips and troubleshooting methods.
The rising concerns regarding elevated CPU consumption from the Antimalware Service Executable have become prevalent among Windows users. Often referred to as MsMpEng, this background process plays a pivotal role in safeguarding your device through continuous malware scanning. However, its resource-intensive operations can detract from your system’s efficiency, particularly when real-time protection is enabled. Many users may face related challenges, including high disk usage linked to this security feature. In this guide, we will explore these issues in detail and provide valuable insights on managing and optimizing your CPU resources effectively.
Understanding MsMpEng High CPU Usage
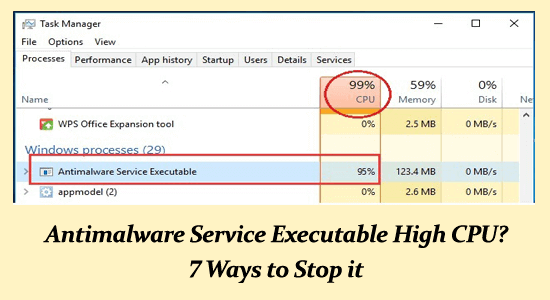
High CPU usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable, often known as MsMpEng, arises primarily when Windows Defender performs its real-time protection tasks. This essential service continuously scans files and applications for potential threats, which is critical for your system’s security. However, when the system is undergoing updates or if multiple files are being scanned, this process can lead to significant resource consumption, often resulting in sluggishness and reduced performance. Users must understand that while this proactive measure is designed to keep malware at bay, it can sometimes backfire, leading to frustration for those working on resource-limited machines.
One common trigger for excessive CPU usage is the scanning of large files or a high volume of data. If you have a sizable media library or frequently download large programs, MsMpEng may spend a considerable amount of time scanning these files. Additionally, on computers with limited RAM or slower processors, even routine scanning can disrupt normal operations, making it essential for users to monitor and manage how frequently and when scans occur.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Antimalware Service Executable high CPU usage?
The Antimalware Service Executable, known as MsMpEng.exe, often shows high CPU usage due to its real-time protection feature that continuously scans files and applications for malware threats. This incessant scanning, especially during updates or when new files are accessed, can heavily tax system resources, leading to elevated CPU utilization.
How can I fix Antimalware Service high disk usage issues?
To resolve high disk usage from the Antimalware Service Executable, you can disable Windows Defender via Command Prompt, turn off real-time protection, or add MsMpEng.exe to the exclusion list in Windows Defender settings. Additionally, performing a clean boot can help identify conflicting applications causing the issue.
Is MsMpEng.exe a virus or malware?
No, MsMpEng.exe is not a virus. It is the legitimate Antimalware Service Executable integral to Windows Defender. It operates in the background to safeguard your system from malware, and its presence is essential for maintaining your device’s security.
What should I do if Antimalware Service Executable is using too much CPU?
If the Antimalware Service Executable is using excessive CPU resources, try temporarily disabling it, checking for software conflicts, or scheduling scans during less active hours. Additionally, consider using a third-party antivirus solution to alleviate high CPU usage associated with Windows Defender.
How do I disable Antimalware Service (MsMpEng) on Windows 10?
To disable the Antimalware Service Executable on Windows 10, you can use Command Prompt to alter its registry settings or simply turn off real-time protection in Windows Security settings. Altering the scan schedule can also help reduce CPU usage.
Can I stop Antimalware Service Executable from running in the background?
Yes, it’s possible to stop the Antimalware Service Executable from running in the background by disabling Windows Defender through Command Prompt or Task Manager. However, ensure that you have another antivirus solution installed to protect against malware.
What are the recommendations to reduce CPU usage on Windows 10 due to Antimalware Service?
To reduce CPU usage from the Antimalware Service Executable, consider adding it to the exclusion list, adjusting scan schedules, or performing a clean boot to disable conflicting startup applications that may contribute to high CPU usage.
Is it safe to disable the Antimalware Service Executable process?
While you can disable the Antimalware Service Executable, doing so may expose your system to potential threats if you do not have another active antivirus solution. Before disabling it, ensure your PC security is adequately covered by reviewing your protection settings.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Antimalware Service Executable Process | Known as MsMpEng, it is responsible for the real-time defense of Windows operating systems. |
| High CPU Usage Causes | Real-time scanning activities of Windows Defender can lead to high disk and CPU usage. |
| Fixing Solutions | 1. Disable Windows Defender via Command Prompt or Registry Editor. 2. Turn off real-time protection. 3. Schedule antivirus scans to improve performance. 4. Add Antimalware Service Executable to Exclusions. 5. Perform a clean boot to prevent conflicting software. |
| Recommended Software | Consider using Advanced System Repair for fixing system issues and optimizing performance. |
Summary
Antimalware Service Executable high CPU issues are a significant concern for many Windows users. The process, crucial for the security provided by Windows Defender, often leads to excessive CPU usage due to its continuous real-time scanning. This can severely impact the performance of your computer. To tackle high CPU consumption from Antimalware Service Executable, users can take several proactive steps such as disabling real-time protection, scheduling scans for off-peak hours, or adding the executable to the exclusion list. By exploring these solutions, users can effectively manage CPU usage and ensure their systems run smoothly without compromising security.
Interesting read about the Antimalware Service Executable and its impact on CPU usage. I’ve also noticed my system slowing down when Windows Defender is actively scanning. The suggestions in this article seem practical and could really help optimize performance. It’s good to know there are ways to manage this without compromising security. How effective are these solutions in the long term?